
The goal is figuring out if you still have urine in the bladder after voiding. In any case, this is a noninvasive evaluation. A postvoid residual with catheterization is another alternative, but it is not commonly performed. In simple words, this exam is a variation of the usual bladder ultrasound. If your doctor has ordered a postvoid residual measurement, you may wonder what it is about. It also measures how much residual urine volume retains in the bladder (1). It is not only a reliable exam to see if you have post-void residual urine. Postvoid residual volume measurements are helpful to detect and diagnose all of the conditions above. This is usually a nerve problem sending the wrong signals to the brain.
Residual volume full#
It can be a kidney stone or an enlarged prostate. What happens when the postvoid residual volume is higher than normal?
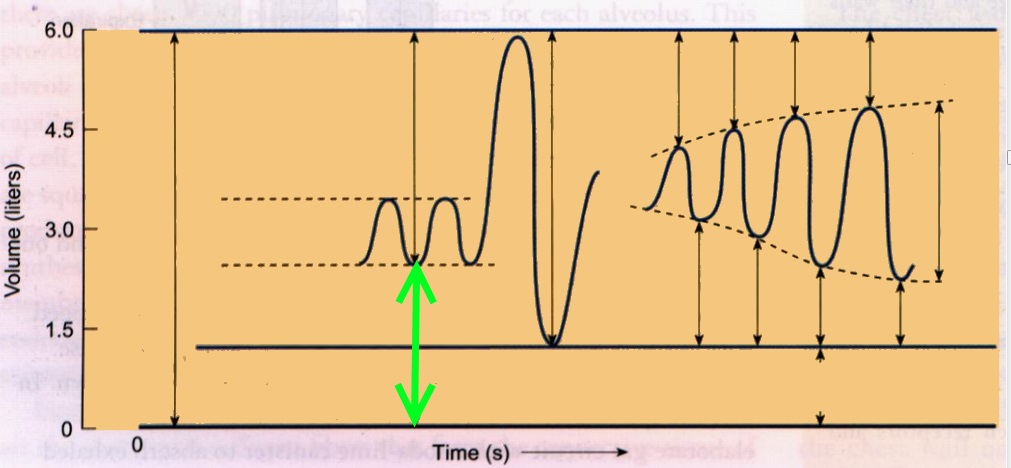
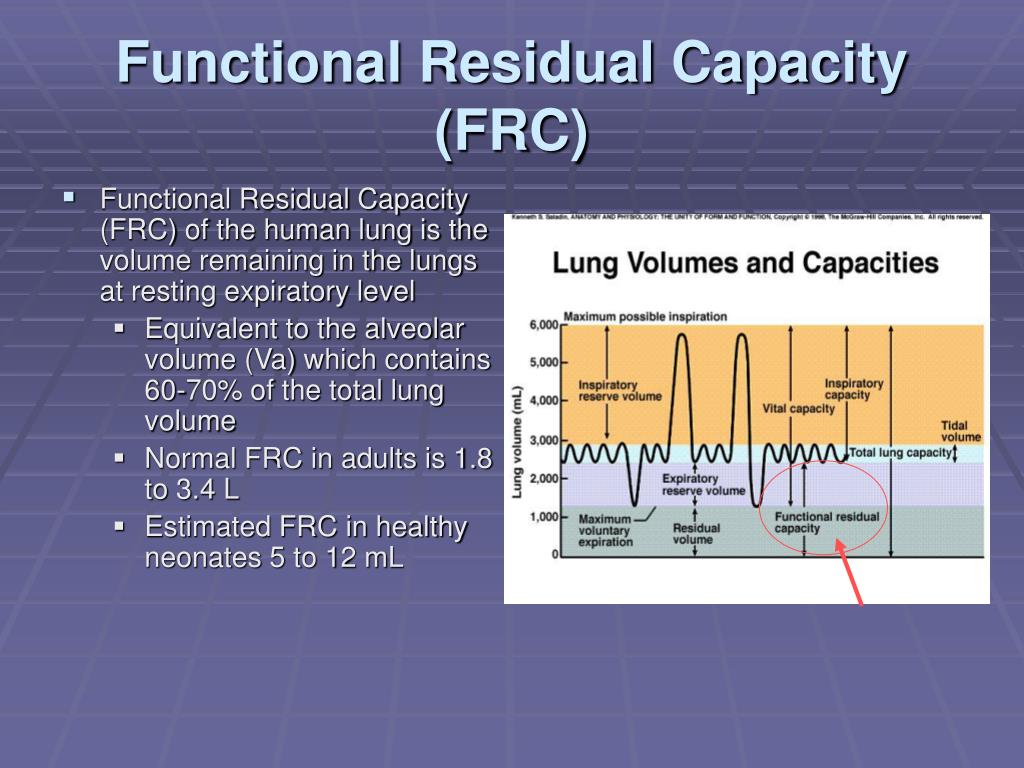
Postvoid residual is what is in the bladder after this struggle between the pressure inside and outside the body. As the pressure reduces, the urine flow is slower, and it finally stops. We can also increase the abdominal pressure to push the urine to the outside. The contraction of the bladder walls increases this pressure as the urine leaks out. The urine pressure is what triggers the need for voiding in the first place. The voiding scheme mentioned above is what happens in healthy individuals, and the bladder’s urine pressure plays a significant role. Then, the stream is slower but steady until you’re done. The first half of the urinary stream is very rapid because of the pressure in the bladder.This releases the urine, which goes through the urethra directly to the outside. When you’re voiding, the bladder wall contracts, and the bladder sphincter opens up.As the bladder becomes full, the sensation becomes uncomfortable, and finally, you can’t resist the urge.You can postpone voiding, and the sensation will come and go. The bladder contracts every now and then, increasing the sensation temporarily.It all starts with a full bladder and the sensation of going to the bathroom.To understand more precisely what is postvoid residual and how it works, let’s review the process of urinating: But if you have a urinary obstruction, this volume is abnormally high (1). Actually, there’s always a small volume left in the bladder, even in healthy people. The sensation of not eliminating all the urine in the bladder is real sometimes. Postvoid residual volume (PVR urine volume) is urine that stays in the bladder after voiding. And it is valuable information for anyone who needs a postvoid residual volume measurement and does not know what it is about. It is an explanation for those who feel urine stuck in the urinary bladder. In this article, we’re covering the topic of post-void residual volume. It also has a role in diagnosing neurogenic bladder and other conditions. For example, in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. This exam is routinely done in patients with urinary tract obstruction.
Is it just an idea in your mind, or is it a real and measurable problem? Postvoid Residual Volume is one of the exams that will help you answer this question. Have you had the sensation of keeping urine stored in the bladder after urinating? It is a frustrating sensation because you feel that you’re not done but cannot continue voiding.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
